This article was featured in One Great Story, New York’s reading recommendation newsletter. Sign up here to get it nightly.
When Nicholson Baker published “The Lab-Leak Hypothesis” in January 2021, the subject was still deeply taboo across the American political and journalistic landscape. Since then, the hypothesis has been revived and reconsidered not just by major investigations by the New York Times, The Wall Street Journal, the Washington Post, and The Atlantic but also by the WHO and the U.S. intelligence community. Nearly every point that would later serve as the basis for the public reconsideration of pandemic origins was contained in Baker’s original story, the first of its kind.
I.
Flask Monsters
What happened was fairly simple, I’ve come to believe. It was an accident. A virus spent some time in a laboratory, and eventually it got out. SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, began its existence inside a bat, then it learned how to infect people in a claustrophobic mine shaft, and then it was made more infectious in one or more laboratories, perhaps as part of a scientist’s well-intentioned but risky effort to create a broad-spectrum vaccine. SARS-2 was not designed as a biological weapon. But it was, I think, designed. Many thoughtful people dismiss this notion, and they may be right. They sincerely believe that the coronavirus arose naturally, “zoonotically,” from animals, without having been previously studied, or hybridized, or sluiced through cell cultures, or otherwise worked on by trained professionals. They hold that a bat, carrying a coronavirus, infected some other creature, perhaps a pangolin, and that the pangolin may have already been sick with a different coronavirus disease, and out of the conjunction and commingling of those two diseases within the pangolin, a new disease, highly infectious to humans, evolved. Or they hypothesize that two coronaviruses recombined in a bat, and this new virus spread to other bats, and then the bats infected a person directly — in a rural setting, perhaps — and that this person caused a simmering undetected outbreak of respiratory disease, which over a period of months or years evolved to become virulent and highly transmissible but was not noticed until it appeared in Wuhan.
There is no direct evidence for these zoonotic possibilities, just as there is no direct evidence for an experimental mishap — no written confession, no incriminating notebook, no official accident report. Certainty craves detail, and detail requires an investigation. It has been a full year, 80 million people have been infected, and, surprisingly, no public investigation has taken place. We still know very little about the origins of this disease.
Nevertheless, I think it’s worth offering some historical context for our yearlong medical nightmare. We need to hear from the people who for years have contended that certain types of virus experimentation might lead to a disastrous pandemic like this one. And we need to stop hunting for new exotic diseases in the wild, shipping them back to laboratories, and hot-wiring their genomes to prove how dangerous to human life they might become.
Over the past few decades, scientists have developed ingenious methods of evolutionary acceleration and recombination, and they’ve learned how to trick viruses, coronaviruses in particular, those spiky hairballs of protein we now know so well, into moving quickly from one species of animal to another or from one type of cell culture to another. They’ve made machines that mix and mingle the viral code for bat diseases with the code for human diseases — diseases like SARS, severe acute respiratory syndrome, for example, which arose in China in 2003,While the first documented case of SARS was in November 2002, it became a pandemic in 2003, and the WHO issued its first alert about the virus in March of that year. and MERS, Middle East respiratory syndrome, which broke out a decade later and has to do with bats and camels. Some of the experiments — “gain of function” experiments — aimed to create new, more virulent, or more infectious strains of diseases in an effort to predict and therefore defend against threats that might conceivably arise in nature. The term gain of function is itself a euphemism; the Obama White House more accurately described this work as “experiments that may be reasonably anticipated to confer attributes to influenza, MERS, or SARS viruses such that the virus would have enhanced pathogenicity and/or transmissibility in mammals via the respiratory route.” The virologists who carried out these experiments have accomplished amazing feats of genetic transmutation, no question, and there have been very few publicized accidents over the years. But there have been some.
And we were warned, repeatedly. The intentional creation of new microbes that combine virulence with heightened transmissibility “poses extraordinary risks to the public,” wrote infectious-disease experts Marc Lipsitch and Thomas Inglesby in 2014. “A rigorous and transparent risk-assessment process for this work has not yet been established.” That’s still true today. In 2012, in Bulletin of the Atomic Scientists, Lynn Klotz warned that there was an 80 percent chance, given how many laboratories were then handling virulent viro-varietals, that a leak of a potential pandemic pathogen would occur sometime in the next 12 years.
A lab accident — a dropped flask, a needle prick, a mouse bite, an illegibly labeled bottle — is apolitical. Proposing that something unfortunate happened during a scientific experiment in Wuhan — where COVID-19 was first diagnosed and where there are three high-security virology labs, one of which held in its freezers the most comprehensive inventory of sampled bat viruses in the world — isn’t a conspiracy theory. It’s just a theory. It merits attention, I believe, alongside other reasoned attempts to explain the source of our current catastrophe.
II.
“A Reasonable Chance”
From early 2020, the world was brooding over the origins of COVID-19. People were reading research papers, talking about what kinds of live animals were or were not sold at the Wuhan seafood market — wondering where the new virus had come from.
Meanwhile, things got strange all over the world. The Chinese government shut down transportation and built hospitals at high speed. There were video clips of people who’d suddenly dropped unconscious in the street. A doctor on YouTube told us how we were supposed to scrub down our produce when we got back from the supermarket. A scientist named Shi Zhengli of the Wuhan Institute of Virology published a paper saying that the novel coronavirus was 96 percent identical to a bat virus, RaTG13, found in Yunnan province in southern China. On March 13, I wrote in my journal that there seemed to be something oddly artificial about the disease: “It’s too airborne — too catching — it’s something that has been selected for infectivity. That’s what I suspect. No way to know so no reason to waste time thinking about it.”
This was just a note to self — at the time, I hadn’t interviewed scientists about SARS-2 or read their research papers. But I did know something about pathogens and laboratory accidents; I published a book last year, Baseless, that talks about some of them. The book is named after a Pentagon program, Project Baseless, whose goal, as of 1951, was to achieve “an Air Force–wide combat capability in biological and chemical warfare at the earliest possible date.”
A vast treasure was spent by the U.S. on the amplification and aerial delivery of diseases — some well known, others obscure and stealthy. America’s biological-weapons program in the ’50s had A1-priority status, as high as nuclear weapons. In preparation for a total war with a numerically superior communist foe, scientists bred germs to be resistant to antibiotics and other drug therapies, and they infected lab animals with them, using a technique called “serial passaging,” in order to make the germs more virulent and more catching.
And along the way, there were laboratory accidents. By 1960, hundreds of American scientists and technicians had been hospitalized, victims of the diseases they were trying to weaponize. Charles Armstrong, of the National Institutes of Health, one of the consulting founders of the American germ-warfare program, investigated Q fever three times, and all three times, scientists and staffers got sick. In the anthrax pilot plant at Camp Detrick, Maryland, in 1951, a microbiologist, attempting to perfect the “foaming process” of high-volume production, developed a fever and died. In 1964, veterinary worker Albert Nickel fell ill after being bitten by a lab animal.
His wife wasn’t told that he had Machupo virus, or Bolivian hemorrhagic fever. “I watched him die through a little window to his quarantine room at the Detrick infirmary,” she said.
In 1977, a worldwide epidemic of influenza A began in Russia and China; it was eventually traced to a sample of an American strain of flu preserved in a laboratory freezer since 1950. In 1978, a hybrid strain of smallpox killed a medical photographer at a lab in Birmingham, England; in 2007, live foot-and-mouth disease leaked from a faulty drainpipe at the Institute for Animal Health in Surrey. In the U.S., “more than 1,100 laboratory incidents involving bacteria, viruses and toxins that pose significant or bioterror risks to people and agriculture were reported to federal regulators during 2008 through 2012,” reported USA Today in an exposé published in 2014.
In 2015, the Department of Defense discovered that workers at a germ-warfare testing center in Utah had mistakenly sent close to 200 shipments of live anthrax to laboratories throughout the United States and also to Australia, Germany, Japan, South Korea, and several other countries over the past 12 years. In 2019, laboratories at Fort Detrick — where “defensive” research involves the creation of potential pathogens to defend against — were shut down for several months by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for “breaches of containment.” They reopened in December 2019.
High-containment laboratories have a whispered history of near misses. Scientists are people, and people have clumsy moments and poke themselves and get bitten by the enraged animals they are trying to nasally inoculate. Machines can create invisible aerosols, and cell solutions can become contaminated. Waste systems don’t always work properly. Things can go wrong in a hundred different ways.
Hold that human fallibility in your mind. And then consider the cautious words of Alina Chan, a scientist who works at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard. “There is a reasonable chance that what we are dealing with is the result of a lab accident,” Chan told me in July of last year. There was also, she added, a reasonable chance that the disease had evolved naturally — both were scientific possibilities. “I don’t know if we will ever find a smoking gun, especially if it was a lab accident. The stakes are so high now. It would be terrifying to be blamed for millions of cases of COVID-19 and possibly up to a million deaths by year end, if the pandemic continues to grow out of control. The Chinese government has also restricted their own scholars and scientists from looking into the origins of SARS-CoV-2. At this rate, the origin of SARS-CoV-2 may just be buried by the passage of time.”
I asked Jonathan A. King, a molecular biologist and biosafety advocate from MIT, whether he’d thought lab accident when he first heard about the epidemic. “Absolutely, absolutely,” King answered. Other scientists he knew were concerned as well. But scientists, he said, in general were cautious about speaking out. There were “very intense, very subtle pressures” on them not to push on issues of laboratory biohazards. Collecting lots of bat viruses, and passaging those viruses repeatedly through cell cultures, and making bat-human viral hybrids, King believes, “generates new threats and desperately needs to be reined in.”
“All possibilities should be on the table, including a lab leak,” a scientist from the NIH, Philip Murphy — chief of the Laboratory of Molecular Immunology — wrote me recently. Nikolai Petrovsky, a professor of endocrinology at Flinders University College of Medicine in Adelaide, Australia, said in an email, “There are indeed many unexplained features of this virus that are hard if not impossible to explain based on a completely natural origin.” Richard Ebright, a molecular biologist at Rutgers University, wrote that he’d been concerned for some years about the Wuhan laboratory and about the work being done there to create “chimeric” (i.e., hybrid) SARS-related bat coronaviruses “with enhanced human infectivity.” Ebright said, “In this context, the news of a novel coronavirus in Wuhan ***screamed*** lab release.”
III.
“No Credible Evidence”
The new disease, as soon as it appeared, was intercepted — stolen and politicized by people with ulterior motives. The basic and extremely interesting scientific question of what happened was sucked up into an ideological sharknado.
Some Americans boycotted Chinese restaurants; others bullied and harassed Asian Americans. Steve Bannon, broadcasting from his living room, in a YouTube series called War Room, said that the Chinese Communist Party had made a biological weapon and intentionally released it. He called it the “CCP virus.” And his billionaire friend and backer, Miles Guo, a devoted Trump supporter, told a right-wing website that the communists’ goal was to “use the virus to infect selective people in Hong Kong, so that the Chinese Communist Party could use it as an excuse to impose martial law there and ultimately crush the Hong Kong pro-democracy movement. But it backfired terribly.”
In The Lancet, in February, a powerful counterstatement appeared, signed by 27 scientists. “We stand together to strongly condemn conspiracy theories suggesting that COVID-19 does not have a natural origin,” the statement said. “Scientists from multiple countries have published and analyzed genomes of the causative agent, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and they overwhelmingly conclude that this coronavirus originated in wildlife, as have so many other emerging pathogens.”
The behind-the-scenes organizer of this Lancet statement, Peter Daszak, is a zoologist and bat-virus sample collector and the head of a New York nonprofit called EcoHealth Alliance — a group that (as veteran science journalist Fred Guterl explained later in Newsweek) has channeled money from the National Institutes of Health to Shi Zhengli’s laboratory in Wuhan, allowing the lab to carry on recombinant research into diseases of bats and humans. “We have a choice whether to stand up and support colleagues who are being attacked and threatened daily by conspiracy theorists or to just turn a blind eye,” Daszak said in February in Science magazine.
Vincent Racaniello, a professor at Columbia and a co-host of a podcast called This Week in Virology, said on February 9 that the idea of an accident in Wuhan was “complete bunk.” The coronavirus was 96 percent similar to a bat virus found in 2013, Racaniello said. “It’s not a man-made virus. It wasn’t released from a lab.”
Racaniello’s dismissal was seconded by a group of scientists from Ohio State, the University of Pennsylvania, and the University of North Carolina, who put out a paper in Emerging Microbes and Infections to quiet the “speculations, rumors, and conspiracy theories that SARS-CoV-2 is of laboratory origin.” There was “currently no credible evidence” that SARS-2 leaked from a lab, these scientists said, using a somewhat different argument from Racaniello’s. “Some people have alleged that the human SARS-CoV-2 was leaked directly from a laboratory in Wuhan where a bat CoV (RaTG13) was recently reported,” they said. But RaTG13 could not be the source because it differed from the human SARS-2 virus by more than a thousand nucleotides. One of the paper’s authors, Susan Weiss, told the Raleigh News & Observer, “The conspiracy theory is ridiculous.”
The most influential natural-origin paper, “The Proximal Origin of SARS-CoV-2,” by a group of biologists that included Kristian Andersen of Scripps Research, appeared online in a preliminary version in mid-February.
“We do not believe any type of laboratory-based scenario is plausible,” the scientists said. Why? Because molecular-modeling software predicted that if you wanted to optimize an existing bat virus so that it would replicate well in human cells, you would arrange things a different way than how the SARS-2 virus actually does it — even though the SARS-2 virus does an extraordinarily good job of replicating in human cells. The laboratory-based scenario was implausible, the paper said, because, although it was true that the virus could conceivably have developed its unusual genetic features in a laboratory, a stronger and “more parsimonious” explanation was that the features came about through some kind of natural mutation or recombination. “What we think,” explained one of the authors, Robert F. Garry of Tulane University, on YouTube, “is that this virus is a recombinant. It probably came from a bat virus, plus perhaps one of these viruses from the pangolin.” Journalists, for the most part, echoed the authoritative pronouncements of Daszak, Racaniello, Weiss, Andersen, and other prominent natural-originists. “The balance of the scientific evidence strongly supports the conclusion that the new coronavirus emerged from nature — be it the Wuhan market or somewhere else,” said the Washington Post’s “Fact Checker” column. “Dr. Fauci Again Dismisses Wuhan Lab As Source of Coronavirus,” said CBS News, posting a video interview of Anthony Fauci by National Geographic. “If you look at the evolution of the virus in bats, and what’s out there now,” Fauci said, “it’s very, very strongly leaning toward ‘This could not have been artificially or deliberately manipulated’ — the way the mutations have naturally evolved.”
Everyone took sides; everyone thought of the new disease as one more episode in an ongoing partisan struggle. Think of Mike Pompeo, that landmass of Cold War truculence; think of Donald Trump himself. They stood at their microphones saying, in a winking, I-know-something-you-don’t-know sort of way, that this disease escaped from a Chinese laboratory. Whatever they were saying must be wrong. It became impermissible, almost taboo, to admit that, of course, SARS-2 could have come from a lab accident. “The administration’s claim that the virus spread from a Wuhan lab has made the notion politically toxic, even among scientists who say it could have happened,” wrote science journalist Mara Hvistendahl in the Intercept.
IV.
“Is It a Complete Coincidence?”
Even so, in January and February of 2020, there were thoughtful people who were speaking up, formulating their perplexities.
One person was Sam Husseini, an independent journalist. He went to a CDC press conference at the National Press Club on February 11, 2020. By then, 42,000 people had gotten sick in China and more than a thousand had died. But there were only 13 confirmed cases in the U.S. Halfway through the Q&A period, Husseini went to the microphone and asked the CDC’s representative, Anne Schuchat, where the virus had come from. His head was spinning, he told me later.
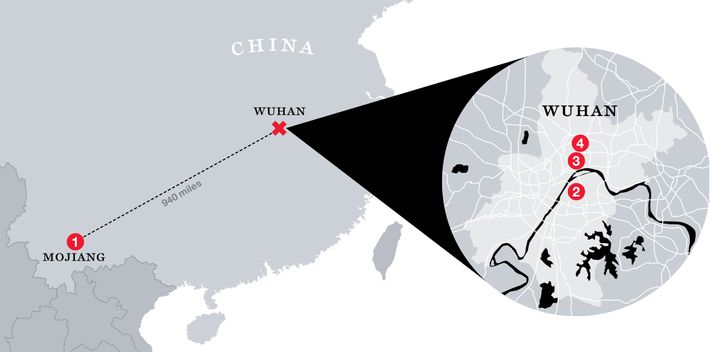
“Obviously the main concern is how to stop the virus,” Husseini said; nonetheless, he wanted to know more about its source. “Is it the CDC’s contention,” he asked, “that there’s absolutely no relation to the BSL-4 lab in Wuhan? It’s my understanding that this is the only place in China with a BSL-4 lab. We in the United States have, I think, two dozen or so, and there have been problems and incidents.” (A BSL-4 laboratory is a maximum-security biosafety-level-four facility, used to house research on the most dangerous known pathogens. New York has confirmed there are at least 11 BSL-4 facilities currently operating in the U.S.) Husseini hastened to say that he wasn’t implying that what happened in Wuhan was in any way intentional. “I’m just asking, Is it a complete coincidence that this outbreak happened in the one city in China with a BSL-4 lab?”
Schuchat thanked Husseini for his questions and comments. Everything she’d seen was quite consistent with a natural, zoonotic origin for the disease, she said.
That same month, a group of French scientists from Aix-Marseille University posted a paper describing their investigation of a small insertion in the genome of the new SARS-2 virus. The virus’s spike protein contained a sequence of amino acids that formed what Etienne Decroly and colleagues called a “peculiar furin-like cleavage site” — a chemically sensitive region on the lobster claw of the spike protein that would react in the presence of an enzyme called furin, which is a type of protein found everywhere within the human body, but especially in the lungs. When the spike senses human furin, it shudders, chemically speaking, and the enzyme opens the protein, commencing the tiny morbid ballet whereby the virus burns a hole in a host cell’s outer membrane and finds its way inside.
The code for this particular molecular feature — not found in SARS or any SARS-like bat viruses, but present in a slightly different form in the more lethal MERS virus — is easy to remember because it’s a roar: “R-R-A-R.” The letter code stands for amino acids: arginine, arginine, alanine, and arginine. Its presence, so Decroly and his colleagues observed, may heighten the “pathogenicity” — that is, the god-awfulness — of a disease.
Botao Xiao, a professor at the South China University of Technology, posted a short paper on a preprint server titled “The Possible Origins of 2019-nCoV Coronavirus.” Two laboratories, the Wuhan Center for Disease Control and Prevention (WHCDC) and the Wuhan Institute of Virology, were not far from the seafood market, which was where the disease was said to have originated, Xiao wrote — in fact, the WHCDC was only a few hundred yards away from the market — whereas the horseshoe bats that hosted the disease were hundreds of miles to the south. (No bats were sold in the market, he pointed out.) It was unlikely, he wrote, that a bat would have flown to a densely populated metropolitan area of 15 million people. “The killer coronavirus probably originated from a laboratory in Wuhan,” Xiao believed. He urged the relocation of “biohazardous laboratories” away from densely populated places. His article disappeared from the server.
And late in the month, a professor at National Taiwan University, Fang Chi-tai, gave a lecture on the coronavirus in which he described the anomalous R-R-A-R furin cleavage site. The virus was “unlikely to have four amino acids added all at once,” Fang said — natural mutations were smaller and more haphazard, he argued. “From an academic point of view, it is indeed possible that the amino acids were added to COVID-19 in the lab by humans.” When the Taiwan News published an article about Fang’s talk, Fang disavowed his own comments, and the video copy of the talk disappeared from the website of the Taiwan Public Health Association. “It has been taken down for a certain reason,” the association explained. “Thank you for your understanding.”
V.
“A Serious Shortage of Appropriately Trained Technicians”
In the spring, I did some reading on coronavirus history. Beginning in the 1970s, dogs, cows, and pigs were diagnosed with coronavirus infections; dog shows were canceled in 1978 after 25 collies died in Louisville, Kentucky. New varieties of coronaviruses didn’t start killing humans, though, until 2003 — that’s when restaurant chefs, food handlers, and people who lived near a live-animal market got sick in Guangzhou, in southern China, where the shredded meat of a short-legged raccoonlike creature, the palm civet, was served in a regional dish called “dragon-tiger-phoenix soup.” The new disease, SARS, spread alarmingly in hospitals, and it reached 30 countries and territories. More than 800 people died; the civet-borne virus was eventually traced to horseshoe bats.
Later, smaller outbreaks of SARS in Taiwan, Singapore, and China’s National Institute of Virology in Beijing were all caused by laboratory accidents. Of the Beijing Virology Institute, the World Health Organization’s safety investigators wrote, in May 2004, that they had “serious concerns about biosafety procedures.” By one account, a SARS storage room in the Beijing lab was so crowded that the refrigerator holding live virus was moved out to the hallway. “Scientists still do not fully understand exactly where or how SARS emerged 18 months ago,” wrote Washington Post reporter David Brown in June 2004. “But it is clear now that the most threatening source of the deadly virus today may be places they know intimately — their own laboratories.”
MERS arose in 2012, possibly spread by camels that had contracted the disease from bats or bat guano, then passed it to human drinkers of raw camel milk and butchers of camel meat. It was an acute sickness, with a high fatality rate, mostly confined to Saudi Arabia. Like SARS, MERS ebbed quickly — it all but disappeared outside the Middle East, except for an outbreak in 2015 at the Samsung Medical Center in South Korea, where a single case of MERS led to more than 180 infections, many involving hospital workers.
In January 2015, the brand-new BSL-4 lab in Wuhan, built by a French contractor, celebrated its opening, but full safety certification came slowly. According to State Department cables from 2018 leaked to the Washington Post, the new BSL-4 lab had some start-up problems, including “a serious shortage of appropriately trained technicians and investigators needed to safely operate this high-containment laboratory.” The staff had gotten some training at a BSL-4 lab in Galveston, Texas, but they were doing potentially dangerous work with SARS-like viruses, the memo said, and they needed more help from the U.S.
In November or December of 2019, the novel coronavirus began to spread. Chinese scientists initially named it “Wuhan seafood market pneumonia virus,” but soon that idea went away. The market, closed and decontaminated by Chinese officials on January 1, 2020, was an amplifying hub, not the source of the outbreak, according to several studies by Chinese scientists. Forty-five percent of the earliest SARS-2 patients had no link with the market.
VI.
Emergence
Now let’s take a step back. AIDS, fatal and terrifying and politically charged, brought on a new era in government-guided vaccine research, under the guidance of Anthony Fauci. A virologist at Rockefeller University, Stephen S. Morse, began giving talks on “emerging viruses” — other plagues that might be in the process of coming out of nature’s woodwork. In 1992, Richard Preston wrote a horrific account of one emergent virus, Ebola, in The New Yorker, which became a best-selling book in 1994; Laurie Garrett’s The Coming Plague: Newly Emerging Diseases in a World Out of Balance appeared that same year and was also a best seller. The idea seemed to be everywhere: We were on the verge of a wave of zoonotic, emergent plagues.
This new, useful term, emerging, began to glow in the research papers of some coronavirologists, who were out of the spotlight, working on common colds and livestock diseases. The term was useful because it was fluid. An emerging disease could be real and terrifying, as AIDS was — something that had just arrived on the medical scene and was confounding our efforts to combat it — or it could be a disease that hadn’t arrived, and might never arrive, but could be shown in a laboratory to be waiting in the wings, just a few mutations away from a human epidemic. It was real and unreal at the same time — a quality that was helpful when applying for research grants.
Take, for instance, this paper from 1995: “High Recombination and Mutation Rates in Mouse Hepatitis Viruses Suggest That Coronaviruses May Be Potentially Important Emerging Viruses.” It was written by Dr. Ralph Baric and his bench scientist, Boyd Yount, at the University of North Carolina. Baric, a gravelly voiced former swim champion, described in this early paper how his lab was able to train a coronavirus, MHV, which causes hepatitis in mice, to jump species, so that it could reliably infect BHK (baby-hamster kidney) cell cultures. They did it using serial passaging: repeatedly dosing a mixed solution of mouse cells and hamster cells with mouse-hepatitis virus, while each time decreasing the number of mouse cells and upping the concentration of hamster cells. At first, predictably, the mouse-hepatitis virus couldn’t do much with the hamster cells, which were left almost free of infection, floating in their world of fetal-calf serum. But by the end of the experiment, after dozens of passages through cell cultures, the virus had mutated: It had mastered the trick of parasitizing an unfamiliar rodent. A scourge of mice was transformed into a scourge of hamsters. And there was more: “It is clear that MHV can rapidly alter its species specificity and infect rats and primates,” Baric said. “The resulting virus variants are associated with demyelinating diseases in these alternative species.” (A demyelinating disease is a disease that damages nerve sheaths.) With steady prodding from laboratory science, along with some rhetorical exaggeration, a lowly mouse ailment was morphed into an emergent threat that might potentially cause nerve damage in primates. That is, nerve damage in us.
A few years later, in a further round of “interspecies transfer” experimentation, Baric’s scientists introduced their mouse coronavirus into flasks that held a suspension of African-green-monkey cells, human cells, and pig-testicle cells. Then, in 2002, they announced something even more impressive: They’d found a way to create a full-length infectious clone of the entire mouse-hepatitis genome. Their “infectious construct” replicated itself just like the real thing, they wrote.
Not only that, but they’d figured out how to perform their assembly seamlessly, without any signs of human handiwork. Nobody would know if the virus had been fabricated in a laboratory or grown in nature. Baric called this the “no-see’m method,” and he asserted that it had “broad and largely unappreciated molecular biology applications.” The method was named, he wrote, after a “very small biting insect that is occasionally found on North Carolina beaches.”
In 2006, Baric, Yount, and two other scientists were granted a patent for their invisible method of fabricating a full-length infectious clone using the seamless, no-see’m method. But this time, it wasn’t a clone of the mouse-hepatitis virus — it was a clone of the entire deadly human SARS virus, the one that had emerged from Chinese bats, via civets, in 2002. The Baric Lab came to be known by some scientists as “the Wild Wild West.” In 2007, Baric said that we had entered “the golden age of coronavirus genetics.”
“I would be afraid to look in their freezers,” one virologist told me.
Baric and Shi Zhengli of the Wuhan Institute of Virology, the two top experts on the genetic interplay between bat and human coronaviruses, began collaborating in 2015.
VII.
“I Had Not Slept a Wink”
Early in the pandemic, Scientific American profiled Shi Zhengli, known in China as the “bat woman.” Shi trapped hundreds of bats in nets at the mouths of caves in southern China, sampled their saliva and their blood, swabbed their anuses, and gathered up their fecal pellets. Several times, she visited and sampled bats in a mine in Mojiang, in southern China, where, in 2012, six men set to work shoveling bat guano were sickened by a severe lung disease, three of them fatally. Shi’s team took the samples back to Wuhan and analyzed whatever fragments of bat virus she could find. In some cases, when she found a sequence that seemed particularly significant, she experimented with it in order to understand how it might potentially infect humans. Some of her work was funded by the National Institutes of Health and some of it by the U.S. Defense Threat Reduction Agency of the Department of Defense via Peter Daszak’s EcoHealth Alliance.
As Shi explained to Scientific American, late in December 2019, she heard from the director of the Wuhan Institute that there was an outbreak of a new disease in the city. Medical samples taken from hospital patients arrived at her lab for analysis. Shi determined that the new virus was related to SARS but even more closely related to a bat disease that her own team had found on a virus-hunting trip: the now-famous RaTG13. Shi was surprised that the outbreak was local, she said: “I had never expected this kind of thing to happen in Wuhan, in central China.” The bat hiding places that she’d been visiting were, after all, as far away as Orlando, Florida, is from New York City. Could this new virus, she wondered, have come from her own laboratory? She checked her records and found no exact matches. “That really took a load off my mind,” she said. “I had not slept a wink for days.”
If one of the first thoughts that goes through the head of a lab director at the Wuhan Institute of Virology is that the new coronavirus could have come from her lab, then we are obliged to entertain the scientific possibility that it could indeed have come from her lab. Right then, there should have been a comprehensive, pockets-inside-out, fully public investigation of the Virology Institute, along with the other important virus labs in Wuhan, including the one close by the seafood market, headquarters of the Wuhan CDC. There should have been interviews with scientists, interviews with biosafety teams, close parsings of laboratory notebooks, freezer and plumbing and decontamination systems checks — everything. It didn’t happen. The Wuhan Institute of Virology closed down its databases of viral genomes, and the Chinese Ministry of Education sent out a directive: “Any paper that traces the origin of the virus must be strictly and tightly managed.”
Shi made some WeChat posts early in 2020. “The novel 2019 coronavirus is nature punishing the human race for keeping uncivilized living habits,” she wrote. “I, Shi Zhengli, swear on my life that it has nothing to do with our laboratory.” She advised those who believed rumors, and gave credence to unreliable scientific papers, to “shut their stinking mouths.”
VIII.
“ ‘Bug to Drug’ in 24 Hours”
It wasn’t only AIDS that changed the way the NIH funded research. The War on Terror also influenced which diseases got the most attention. In the late ’90s, under Bill Clinton and then George W. Bush, biodefense specialists became interested — again — in anthrax. The Defense Threat Reduction Agency built a small anthrax factory in Nevada, using simulants, to demonstrate how easy it would be for a terrorist to build a small anthrax factory. And in the first year of the Bush presidency, the Defense Intelligence Agency wrote up plans to create a vaccine-resistant form of anthrax using state-of-the-art gene-splicery. A front-page article describing these initiatives, “U.S. Germ Warfare Research Pushes Treaty Limits,” appeared in the New York Times on September 4, 2001, one week before 9/11. “Pentagon Says Projects Are Defense, Is Pressing Ahead,” was the subtitle.
After the 9/11 attacks, and the mysterious anthrax mailings that began a week later (which said, “TAKE PENACILIN [sic] NOW / DEATH TO AMERICA / DEATH TO ISRAEL / ALLAH IS GREAT”), the desire for biopreparedness became all consuming. Now there were emerging biothreats from humans as well as from the evolving natural world. Fauci’s anti-terror budget went from $53 million in 2001 to $1.7 billion in 2003. Setting aside his work toward an AIDS vaccine, which was taking longer than he’d foreseen, Fauci said he would be going all out to defend against a suite of known Cold War agents, all of which had been bred and perfected in American weapons programs many years before — brucellosis, anthrax, tularemia, and plague, for instance. “We are making this the highest priority,” Fauci said. “We are really marshaling all available resources.”
Vaccine development had to progress much faster, Fauci believed; he wanted to set up “vaccine systems” and “vaccine platforms,” which could be quickly tailored to defend against a particular emergent strain some terrorist with an advanced biochemistry degree might have thrown together in a laboratory. “Our goal within the next 20 years is ‘bug to drug’ in 24 hours,” Fauci said. “This would specifically meet the challenge of genetically engineered bioagents.” The first Project BioShield contract Fauci awarded was to VaxGen, a California pharmaceutical company, for $878 million worth of shots of anthrax vaccine.
By 2005, so much money was going toward biothreat reduction and preparedness that more than 750 scientists sent a protest letter to the NIH. Their claim was that grants to study canonical biowar diseases — anthrax, plague, brucellosis, and tularemia, all exceptionally rare in the U.S. — had increased by a factor of 15 since 2001, whereas funds for the study of widespread “normal” diseases, of high public-health importance, had decreased.
Fauci was firm in his reply: “The United States through its leaders made the decision that this money was going to be spent on biodefense,” he said. “We disagree with the notion that biodefense concerns are of ‘low public-health significance.’ ”
In 2010, by one count, there were 249 BSL-3 laboratories and seven BSL-4 laboratories in the U.S., and more than 11,000 scientists and staffers were authorized to handle the ultralethal germs on the government’s select pathogen list. And yet the sole bioterrorist in living memory who actually killed American citizens, according to the FBI — the man who sent the anthrax letters — turned out to be one of the government’s own researchers. Bruce Ivins, an eccentric, suicidal laboratory scientist from Ohio who worked in vaccine development at Fort Detrick, allegedly wanted to boost the fear level so as to persuade the government to buy more of the patented, genetically engineered anthrax VaxGen vaccine, of which he was a co-inventor. (See David Willman’s fascinating biography of Ivins, Mirage Man.) Fauci’s staff at NIH funded Ivins’s vaccine laboratory and gave $100 million to VaxGen to accelerate vaccine production. (The NIH’s $878 million contract with VaxGen, however, was quietly canceled in 2006; Ivins, who was never charged, killed himself in 2008.)
“The whole incident amounted to a snake eating its own tail,” wrote Wendy Orent in an August 2008 piece titled “Our Own Worst Bioenemy” in the Los Angeles Times. “No ingenious biowarrior from Al Qaeda sent the lethal envelopes through the U.S. postal system. An American scientist did.” What confirmed Ivins’s guilt, according to the FBI, was that there was a genetic match between the anthrax used in the killings and the strain held at Fort Detrick.
IX.
“Weapons of Mass Disruption”
After SARS appeared in 2003, Ralph Baric’s laboratory moved up the NIH funding ladder. SARS was a “dual use” organism — a security threat and a zoonotic threat at the same time. In 2006, Baric wrote a long, fairly creepy paper on the threat of “weaponizable” viruses. Synthetic biology had made possible new kinds of viral “weapons of mass disruption,” he wrote, involving, for example, “rapid production of numerous candidate bioweapons that can be simultaneously released,” a scattershot terror tactic Baric called the “ ‘survival of the fittest’ approach.”
Baric hoped to find a SARS vaccine, but he couldn’t; he kept looking for it, year after year, supported by the NIH, long after the disease itself had been contained. It wasn’t really gone, Baric believed. Like other epidemics that pop up and then disappear, as he told a university audience some years later, “they don’t go extinct. They are waiting to return.” What do you do if you run a well-funded laboratory, an NIH “center of excellence,” and your emergent virus is no longer actually making people sick? You start squeezing it and twisting it into different shapes. Making it stand on its hind legs and quack like a duck, or a bat. Or breathe like a person.
Baric’s safety record is good — although there was a minor mouse-bite incident in 2016, uncovered by ProPublica — and his motives are beyond reproach: “Safe, universal, vaccine platforms are needed that can be tailored to new pathogens as they emerge, quickly tested for safety, and then strategically used to control new disease outbreaks in human populations,” he wrote in a paper on public health. But the pioneering work he did over the past 15 years — generating tiny eager single-stranded flask monsters and pitting them against human cells, or bat cells, or gene-spliced somewhat-human cells, or monkey cells, or humanized mice — was not without risk, and it may have led others astray.
In 2006, for instance, Baric and his colleagues, hoping to come up with a “vaccine strategy” for SARS, produced noninfectious virus replicon particles (or VRPs) using the Venezuelan-equine-encephalitis virus (another American germ-warfare agent), which they fitted with various SARS spike proteins. Then, wearing Tyvek suits and two pairs of gloves each, and working in a biological safety cabinet in a BSL-3-certified laboratory, they cloned and grew recombinant versions of the original SARS virus in an incubator in a medium that held African-green-monkey cells. When they had grown enough virus, the scientists swapped out one kind of spike protein for a carefully chosen mutant, and they challenged their prototype vaccine with it in mice.
The scientists also tried their infectious SARS clones in something called an air-liquid interface, using a relatively new type of cell culture developed by Raymond Pickles of the University of North Carolina’s Cystic Fibrosis Center. Pickles had perfected a method of emulating the traits of human airway tissue by cultivating cells taken from lung-disease patients — nurturing the culture over four to six weeks in such a way that the cells differentiated and developed a crop of tiny moving hairs, or cilia, on top and goblet cells within that produced real human mucus. In fact, before infecting these HAE (human airway epithelial) cells with a virus, the lab worker must sometimes rinse off some of the accumulated mucus, as if helping the lab-grown tissue to clear its throat. So Baric was exposing and adapting his engineered viruses to an extraordinarily true-to-life environment — the juicy, sticky, hairy inner surface of our breathing apparatus.
SARS-2 seems almost perfectly calibrated to grab and ransack our breathing cells and choke the life out of them. “By the time SARS-CoV-2 was first detected in late 2019, it was already pre-adapted to human transmission,” Alina Chan and her co-authors have written, whereas SARS, when it first appeared in 2003, underwent “numerous adaptive mutations” before settling down. Perhaps viral nature hit a bull’s-eye of airborne infectivity, with almost no mutational drift, no period of accommodation and adjustment, or perhaps some lab worker somewhere, inspired by Baric’s work with human airway tissue, took a spike protein that was specially groomed to colonize and thrive deep in the ciliated, mucosal tunnels of our inner core and cloned it onto some existing viral bat backbone. It could have happened in Wuhan, but — because anyone can now “print out” a fully infectious clone of any sequenced disease — it could also have happened at Fort Detrick, or in Texas, or in Italy, or in Rotterdam, or in Wisconsin, or in some other citadel of coronaviral inquiry. No conspiracy — just scientific ambition, and the urge to take exciting risks and make new things, and the fear of terrorism, and the fear of getting sick. Plus a whole lot of government money.
X.
“Risky Areas for Spillover”
Project Bioshield began to fade by the end of the Bush administration, although the expensive high-containment laboratories, controversial preservers and incubators of past and future epidemics, remain. By 2010, some BioShield projects had dissolved into Obama’s Predict program, which paid for laboratories and staff in 60 “risky areas for spillover” around the world. Jonna Mazet, a veterinary scientist from the University of California, Davis, was in charge of Predict, which was a component of USAID’s “Emerging Pandemic Threats” program. Her far-flung teams collected samples from 164,000 animals and humans and claimed to have found “almost 1,200 potentially zoonotic viruses, among them 160 novel coronaviruses, including multiple SARS- and MERS-like coronaviruses.” The fruits of Predict’s exotic harvest were studied and circulated in laboratories worldwide, and their genetic sequences became part of GenBank, the NIH’s genome database, where any curious RNA wrangler anywhere could quickly synthesize snippets of code and test out a new disease on human cells.
Baric, Jonna Mazet, and Peter Daszak of EcoHealth worked together for years — and Daszak also routed Predict money to Shi Zhengli’s bat-surveillance team in Wuhan through his nonprofit, mingling it with NIH money and money from the U.S. Defense Threat Reduction Agency. In 2013, Mazet announced that Shi Zhengli’s virus hunters, with Predict’s support, had, for the first time, isolated and cultured a live SARS-like virus from bats and demonstrated that this virus could bind to the human ACE2, or “angiotensin-converting enzyme 2,” receptor, which Baric’s laboratory had determined to be the sine qua non of human infectivity. “This work shows that these viruses can directly infect humans and validates our assumption that we should be searching for viruses of pandemic potential before they spill over to people,” Mazet said.
Daszak, for his part, seems to have viewed his bat quests as part of an epic, quasi-religious death match. In a paper from 2008, Daszak and a co-author described Bruegel’s painting The Fall of the Rebel Angels and compared it to the contemporary human biological condition. The fallen angels could be seen as pathogenic organisms that had descended “through an evolutionary (not spiritual) pathway that takes them to a netherworld where they can feed only on our genes, our cells, our flesh,” Daszak wrote. “Will we succumb to the multitudinous horde? Are we to be cast downward into chthonic chaos represented here by the heaped up gibbering phantasmagory against which we rail and struggle?”
XI.
“Lab-Made?”
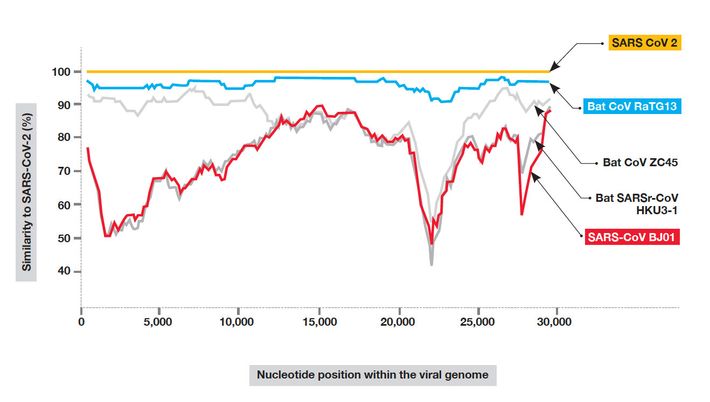
There are, in fact, some helpful points of agreement between zoonoticists — those who believe in a natural origin of the SARS-2 virus — and those who believe that it probably came from a laboratory. Both sides agree, when pressed, that a lab origin can’t be conclusively ruled out and a natural origin can’t be ruled out either — because nature, after all, is capable of improbable, teleological-seeming achievements. Both sides also agree, for the most part, that the spillover event that began the human outbreak probably happened only once, or a few times, quite recently, and not many times over a longer period. They agree that bat virus RaTG13 (named for the Rinolophus affinus bat, from Tongguan, in 2013) is the closest match to the human virus that has yet been found, and that although the two viruses are very similar, the spike protein of the bat virus lacks the features the human spike protein possesses that enable it to work efficiently with human tissue.
Zoonoticists hold that SARS-2’s crucial features — the furin cleavage site and the ACE2 receptor — are the result of a recombinant event involving a bat coronavirus (perhaps RaTG13 or a virus closely related to it) and another, unknown virus. Early on, researchers proposed that it could be a snake sold at the seafood market — a Chinese cobra or a banded krait — but no: Snakes don’t typically carry coronaviruses. Then there was a thought that the disease came from sick smuggled pangolins, because there existed a certain pangolin coronavirus that was, inexplicably, almost identical in its spike protein to the human coronavirus — but then, no: There turned out to be questions about the reliability of the genetic information in that diseased-pangolin data set, on top of which there were no pangolins for sale at the Wuhan market. Then a group from China’s government veterinary laboratory at Harbin tried infecting beagles, pigs, chickens, ducks, ferrets, and cats with SARS-2 to see if they could be carriers. (Cats and ferrets got sick; pigs, ducks, and most dogs did not.)
In September, some scientists at the University of Michigan, led by Yang Zhang, reported that they had created a “computational pipeline” to screen nearly a hundred possible intermediate hosts, including the Sumatran orangutan, the Western gorilla, the Olive baboon, the crab-eating macaque, and the bonobo. All these primates were “permissive” to the SARS-2 coronavirus and should undergo “further experimentational investigation,” the scientists proposed.
Despite this wide-ranging effort, there is at the moment no animal host that zoonoticists can point to as the missing link. There’s also no single, agreed-upon hypothesis to explain how the disease may have traveled from the bat reservoirs of Yunnan all the way to Wuhan, seven hours by train, without leaving any sick people behind and without infecting anyone along the way.
The zoonoticists say that we shouldn’t find it troubling that virologists have been inserting and deleting furin cleavage sites and ACE2-receptor-binding domains in experimental viral spike proteins for years: The fact that virologists have been doing these things in laboratories, in advance of the pandemic, is to be taken as a sign of their prescience, not of their folly. But I keep returning to the basic, puzzling fact: This patchwork pathogen, which allegedly has evolved without human meddling, first came to notice in the only city in the world with a laboratory that was paid for years by the U.S. government to perform experiments on certain obscure and heretofore unpublicized strains of bat viruses — which bat viruses then turned out to be, out of all the organisms on the planet, the ones that are most closely related to the disease. What are the odds?
In July, I discovered a number of volunteer analysts who were doing a new kind of forensic, samizdat science, hunched over the letter code of the SARS-2 genome like scholars deciphering the cuneiform impressions in Linear B tablets. There were the anonymous authors of Project Evidence, on GitHub, who “disavow all racism and violent attacks, including those which are aimed at Asian or Chinese people,” and there was Yuri Deigin, a biotech entrepreneur from Canada, who wrote a massive, lucid paper on Medium, “Lab-Made?,” which illumined the mysteries of the spike protein. Jonathan Latham of the Bioscience Resource Project, with his co-author Allison Wilson, wrote two important papers: one a calm, unsparing overview of laboratory accidents and rash research and the other a close look at the small outbreak of an unexplained viral pneumonia in a bat-infested copper mine in 2012. I corresponded with Alina Chan (now the subject of a nicely turned piece in Boston magazine by Rowan Jacobsen) and with the pseudonymous Billy Bostickson, a tireless researcher whose Twitter photo is a cartoon of an injured experimental monkey, and Monali Rahalkar, of the Agharkar Research Institute in Pune, India, who wrote a paper with her husband, Rahul Bahulikar, that also sheds light on the story of the bat-guano-shoveling men whose virus was remarkably like SARS-2, except that it was not nearly as catching. I talked to Rossana Segreto, a molecular biologist at the University of Innsbruck, whose paper, “Is Considering a Genetic-Manipulation Origin for SARS-CoV-2 a Conspiracy Theory That Must Be Censored?,” co-authored with Yuri Deigin, was finally published in November under a milder title; it argued that SARS-2’s most notable features, the furin site and the human ACE2-binding domain, were unlikely to have arisen simultaneously and “might be the result of lab manipulation techniques such as site directed mutagenesis.” Segreto is also the person who first established that a bat-virus fragment named BtCoV/4991, identified in 2013, was 100 percent identical to the closest known cousin to SARS-CoV-2, the bat virus RaTG13, thereby proving that the virus closest to the SARS-2-pandemic virus was linked back not to a bat cave but to a mine shaft, and that this same virus had been stored and worked on in the Wuhan Institute for years. This made possible the first big investigative piece on SARS-2’s origins, in the Times of London, in July: “Nobody can deny the bravery of scientists who risked their lives harvesting the highly infectious virus,” the Times authors write. “But did their courageous detective work lead inadvertently to a global disaster?”
XII.
“A New, Non-Natural Risk”
In 2011, a tall, confident Dutch scientist, Ron Fouchier, using grant money from Fauci’s group at NIH, created a mutant form of highly pathogenic avian influenza, H5N1, and passaged it ten times through ferrets in order to prove that he could “force” (his word) this potentially fatal disease to infect mammals, including humans, “via aerosols or respiratory droplets.” Fouchier said his findings indicated that these avian influenza viruses, thus forced, “pose a risk of becoming pandemic in humans.”
This experiment was too much for some scientists: Why, out of a desire to prove that something extremely infectious could happen, would you make it happen? And why would the U.S. government feel compelled to pay for it to happen? Late in 2011, Marc Lipsitch of the Harvard School of Public Health got together with several other dismayed onlookers to ring the gong for caution. On January 8, 2012, the New York Times published a scorcher of an editorial, “An Engineered Doomsday.” “We cannot say there would be no benefits at all from studying the virus,” the Times said. “But the consequences, should the virus escape, are too devastating to risk.”
These gain-of-function experiments were an important part of the NIH’s approach to vaccine development, and Anthony Fauci was reluctant to stop funding them. He and Francis Collins, director of the National Institutes of Health, along with Gary Nabel, NIAID director of vaccine research, published an opinion piece in the Washington Post in which they contended that the ferret flu experiments, and others like them, were “a risk worth taking.” “Important information and insights can come from generating a potentially dangerous virus in the laboratory,” they wrote; the work can “help delineate the principles of virus transmission between species.” The work was safe because the viruses were stored in a high-security lab, they believed, and the work was necessary because nature was always coming up with new threats. “Nature is the worst bioterrorist,” Fauci told a reporter. “We know that through history.”
Soon afterward, there followed some distressing screwups in secure federal laboratories involving live anthrax, live smallpox, and live avian influenza. These got attention in the science press. Then Lipsitch’s activists (calling themselves the Cambridge Working Group) sent around a strong statement on the perils of research with “Potential Pandemic Pathogens,” signed by more than a hundred scientists. The work might “trigger outbreaks that would be difficult or impossible to control,” the signers said. Fauci reconsidered, and the White House in 2014 announced that there would be a “pause” in the funding of new influenza, SARS, and MERS gain-of-function research.
Baric, in North Carolina, was not happy. He had a number of gain-of-function experiments with pathogenic viruses in progress. “It took me ten seconds to realize that most of them were going to be affected,” he told NPR. Baric and a former colleague from Vanderbilt University wrote a long letter to an NIH review board expressing their “profound concerns.” “This decision will significantly inhibit our capacity to respond quickly and effectively to future outbreaks of SARS-like or MERS-like coronaviruses, which continue to circulate in bat populations and camels,” they wrote. The funding ban was itself dangerous, they argued. “Emerging coronaviruses in nature do not observe a mandated pause.”
Hoping to smooth over controversy by showing due diligence, the National Science Advisory Board for Biosecurity, founded in the BioShield era under President Bush, paid a consulting firm, Gryphon Scientific, to write a report on gain-of-function research, which by now was simply referred to as GoF. In chapter six of this thousand-page dissertation, published in April 2016, the consultants take up the question of coronaviruses. “Increasing the transmissibility of the coronaviruses could significantly increase the chance of a global pandemic due to a laboratory accident,” they wrote.
The Cambridge Working Group continued to write letters of protest and plead for restraint and sanity. Steven Salzberg, a professor of biomedical engineering at Johns Hopkins, said, “We have enough problems simply keeping up with the current flu outbreaks — and now with Ebola — without scientists creating incredibly deadly new viruses that might accidentally escape their labs.” David Relman of Stanford Medical School said, “It is unethical to place so many members of the public at risk and then consult only scientists — or, even worse, just a small subset of scientists — and exclude others from the decision-making and oversight process.” Richard Ebright wrote that creating and evaluating new threats very seldom increases security: “Doing so in biology — where the number of potential threats is nearly infinite, and where the asymmetry between the ease of creating threats and the difficulty of addressing threats is nearly absolute — is especially counterproductive.” Lynn Klotz wrote, “Awful as a pandemic brought on by the escape of a variant H5N1 virus might be, it is SARS that now presents the greatest risk. The worry is less about recurrence of a natural SARS outbreak than of yet another escape from a laboratory researching it to help protect against a natural outbreak.” Marc Lipsitch argued that gain-of-function experiments can mislead, “resulting in worse not better decisions,” and that the entire gain-of-function debate as overseen by the NIH was heavily weighted in favor of scientific insiders and “distinctly unwelcoming of public participation.”
Nariyoshi Shinomiya, a professor of physiology and nano-medicine at the National Defense Medical College in Japan, offered this warning: “Similar to nuclear or chemical weapons there is no going back once we get a thing in our hands.”
But in the end, Baric was allowed to proceed with his experiments, and the research papers that resulted, showered with money, became a sort of Anarchist’s Cookbook for the rest of the scientific world. In November 2015, Baric and colleagues published a collaboration paper with Shi Zhengli titled “A SARS-like Cluster of Circulating Bat Coronaviruses Shows Potential for Human Emergence.” Into a human SARS virus that they had adapted so that it would work in mice, Baric and Shi et al. inserted the spike protein of a bat virus, SHC014, discovered by Shi in southern China. They dabbed the mice nasally with virus and waited, looking for signs of sickness: “hunching, ruffled fur.” They also infected human airway cells with the mouse-adapted bat-spike-in-a-human-virus backbone. In both mice and human airway cells, the chimeric virus caused a “robust infection.”
This proved, Baric and Shi believed, that you did not need civets or other intermediate hosts in order for bats to cause an epidemic in humans and that therefore all the SARS-like viruses circulating in bat populations “may pose a future threat.” Peter Daszak, who had used Predict funds to pay Shi for her work on the paper, was impressed by this conclusion; the findings, he said, “move this virus from a candidate emerging pathogen to a clear and present danger.”
Richard Ebright was trenchantly unenthusiastic. “The only impact of this work,” he said, “is the creation, in a lab, of a new, non-natural risk.”
Early in 2016, Baric and Shi again collaborated. Shi sent Baric a fresh bat virus spike protein, and Baric inserted it into the backbone of a human SARS virus and then used that infectious clone to attack human airway cells. “The virus readily and efficiently replicated in cultured human airway tissues, suggesting an ability to potentially jump directly to humans,” reported the UNC’s website. This time, they also used the bat-human hybrid virus to infect transgenic humanized mice that grew human ACE2 protein. The mice, young and old, lost weight and died, proving, again, that this particular bat virus was potentially “poised to emerge in human populations.” It was “an ongoing threat,” Baric wrote. But was it? Civets and camels that are exposed to a lot of bat-guano dust may be an ongoing threat and a manageable one. But the bats themselves just want to hang in their caves and not be bothered by frowning sightseers in spacesuits who want to poke Q-tips in their bottoms. This 2016 “poised for human emergence” paper was supported by eight different NIH grants. In 2015, Baric’s lab received $8.3 million from the NIH; in 2016, it received $10.5 million.
Gain-of-function research came roaring back under Trump and Fauci. “The National Institutes of Health will again fund research that makes viruses more dangerous,” said an article in Nature in December 2017. Carrie Wolinetz of the NIH’s office of science policy defended the decision. “These experiments will help us get ahead of viruses that are already out there and pose a real and present danger to human health,” she told The Lancet. The NIH, Wolinetz said, was committed to a leadership role with gain-of-function research internationally. “If we are pursuing this research in an active way, we will be much better positioned to develop protection and countermeasures should something bad happen in another country.”
A reporter asked Marc Lipsitch what he thought of the resumption of NIH funding. Gain-of-function experiments “have done almost nothing to improve our preparedness for pandemics,” he said, “yet they risked creating an accidental pandemic.”
XIII.
“Proximity Is a Problem”
In April, four months into the coronavirus emergency, a deputy director at the NIH wrote an email to EcoHealth Alliance. “You are instructed to cease providing any funds to Wuhan Institute of Virology,” it said. In response, Daszak and the chief scientific officer of New England Biolabs (a company that sells seamless gene-splicing products to laboratories, among other things) got 77 Nobel Prize winners to sign a statement saying that the cancellation deprived the “nation and the world of highly regarded science that could help control one of the greatest health crises in modern history and those that may arise in the future.” Later, as a condition of further funding, the NIH wrote to say it wanted Daszak to arrange an outside inspection of the Wuhan lab and to procure from Wuhan’s scientists a sample of whatever they’d used to sequence the SARS-2 virus. Daszak was outraged (“I am not trained as a private detective”), and again he fought back. He was reluctant to give up his own secrets, too. “Conspiracy-theory outlets and politically motivated organizations have made Freedom of Information Act requests on our grants and all of our letters and emails to the NIH,” he told Nature. “We don’t think it’s fair that we should have to reveal everything we do.”
But Daszak has survived — even prospered. Recently, The Lancet made him the lead investigator in its inquiry into the origins of the pandemic, and the World Health Organization named him to its ten-person origins investigation. (“We’re still close enough to the origin to really find out more details about where it has come from,” Daszak told Nature.)
The NIH has also set up an ambitious new international program, called CREID, which stands for Centers for Research in Emerging Infectious Diseases, and it has put Daszak’s EcoHealth in charge of trapping animals and looking for obscure bat viruses in Singapore, Malaysia, and Thailand. Baric is one of Daszak’s partners in CREID. The virus hunting and collecting, which Richard Ebright likens to “looking for a gas leak with a lighted match,” will continue and widen with U.S. funding. “We’re going to work in remote parts of Malaysia and Thailand to get to the front line of where the next pandemic is going to start,” Daszak told NPR.
In May, an interviewer from the People’s Pharmacy website asked Baric if he had any thoughts on whether the coronavirus began with a natural bat-to-human transfer. “Or was there something a little bit more, perhaps, insidious involved?”
“Well, of course the answers to those questions are in China,” Baric replied. “Exactly how they work in that facility is something that would be very difficult for a Westerner to know,” he said. “The main problems that the Institute of Virology has is that the outbreak occurred in close proximity to that Institute. That Institute has in essence the best collection of virologists in the world that have gone out and sought out, and isolated, and sampled bat species throughout Southeast Asia. So they have a very large collection of viruses in their laboratory. And so it’s — you know — proximity is a problem. It’s a problem.”
Over the course of the fall, and especially after the election muffled Donald Trump’s influence over the country’s public-health apparatus, that proximity problem — and the uncomfortable questions of origins it raised — began to grow somewhat more discussable. The BBC, Le Monde, and Italy’s RAI have all recently taken seriously the scientific possibility of a lab leak. In late October, the World Health Organization convened the first meeting of its second inquiry into the origins of the disease. The WHO’s effort is perhaps the world’s best chance to satisfy its curiosity about goings-on at the Wuhan Institute of Virology and at the Wuhan CDC’s virus lab near the Wuhan seafood market. But, as the New York Times has reported, the WHO’s information gathering has been hindered by Chinese secretiveness since February, when an initial investigative team sent to Beijing was told its members’ access to scientists would be restricted and that it couldn’t visit the seafood market, then considered a hub of the pandemic.
When a BBC video team tried to inspect the Yunnan mine shaft, they found the road to the mine blocked by a strategically parked truck that had “broken down” shortly before they arrived. Reporter John Sudworth asked Daszak, one of the ten members of the second WHO investigative team, whether he would push for access to the Wuhan Institute of Virology. “That’s not my job to do that,” Daszak replied.
In November, David Relman, the Stanford microbiologist, one of the most thoughtful of the voices warning against gain-of-function research, published a paper in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on the urgent need to unravel the origins of COVID-19. “If SARS-CoV-2 escaped from a lab to cause the pandemic,” he wrote, “it will become critical to understand the chain of events and prevent this from happening again.” Conflicts of interest by researchers and administrators will need to be addressed, Relman wrote; to reach the truth, the investigation must be transparent, international, and, as much as possible, unpolitical. “A more complete understanding of the origins of COVID-19 clearly serves the interests of every person in every country on this planet.”
“The world is sitting on a precedent-setting decision right now,” wrote Alina Chan on December 8. “It is unclear if SARS2 is 100 percent natural or emerged due to lab/research activities. If we walk away from this, demonstrating that we cannot effectively investigate its origins, it will pave the way for future COVIDS.”
Just before this issue of New York went to press, I reached Ralph Baric by phone and asked him where he now believed SARS-2 came from. (Anthony Fauci, Shi Zhengli, and Peter Daszak didn’t respond to emails, and Kristian Andersen said he was busy with other things.) Baric said he still thought the virus came from bats in southern China, perhaps directly, or possibly via an intermediate host, although the smuggled pangolins, in his view, were a red herring. The disease evolved in humans over time without being noticed, he suspected, becoming gradually more infectious, and eventually a person carried it to Wuhan “and the pandemic took off.” Then he said, “Can you rule out a laboratory escape? The answer in this case is probably not.”
XIV.
Transmission
So how did we actually get this disease?
Here’s what I think happened. In April 2012, in a copper mine in Mojiang, China, three men were given an awful job — they were told to shovel bat guano out of a mine shaft. They went to work and shoveled guano for seven hours a day in the confined, insufficiently ventilated space of the mine shaft, and by the end of the week, they were sick with a viral pneumonia of unknown etiology. Three more, younger shovelers were hired to replace the ones who were out sick.
The viral load in their lungs was so huge, because of all the guano dust, that their lungs became a kind of accelerated laboratory passaging experiment, as Jonathan Latham and Allison Wilson have written, forcing the virus to switch its allegiance from bats to humans. SARS experts were consulted, and the disease was judged to be SARS-like but not SARS. It was something new. (Shi Zhengli told Scientific American that the guano shovelers had died of a fungal disease, but, as Monali Rahalkar pointed out, they were treated with antivirals, and their symptoms were consistent with viral pneumonia with attendant secondary fungal infections.)
Although it was a severe disease, and in the end three of the shovelers died, there was no resultant epidemic. It was actually a case of industrial overexposure to an infectious substance — what we might call a massive OSHA violation. The bat disease that the men encountered wasn’t necessarily all that dangerous except in an environment of immunosuppressive overload.
Peter Daszak and Shi Zhengli were interested, of course, because this unidentified coronavirus disease involved bats and people. Of the fragmentary bits of virus Shi retrieved from the mine shaft, one was SARS-like, and Shi sequenced it and called it BtCoV/4991 and published a paper about it. Several times — in 2016 and 2018 and 2019 — this most interesting sample, a portion of what we now know as RaTG13, was taken out of the freezers in Shi’s lab and worked on in undisclosed ways. (Peter Daszak claims that these samples have disintegrated and can’t be validated or studied.) Samples of the nameless human disease also traveled back to the Wuhan Institute of Virology — few specifics about these valuable specimens have been released by Chinese sources, however.
This is the period in the story that demands a very close investigation, when chimeric assemblages may have been created and serially passaged, using BtCoV/4991, a.k.a. RaTG13, and other bat viruses, perhaps along with forms of the human virus. It’s when Shi and Baric both published papers that were about what happened when you hot-swapped mutant spike proteins between bat viruses and human viruses.
The link, via the renamed sample BtCoV/4991, to the copper mine is of exceptional importance because of the one huge difference between the unnamed guano shovelers’ virus and the SARS-2 virus that is now ravaging, for example, California: transmissibility. Airborne human-to-human transmissibility — the kind of thing that gain-of-functioneers like Ron Fouchier and Ralph Baric were aiming at, in order to demonstrate what Baric called “lurking threats” — is COVID-19’s crucial distinguishing feature. If six men had gotten extremely sick with COVID-19 back in 2012 in southern China, doctors and nurses in the hospital where they lay dying would likely have gotten sick as well. There might have been hundreds or thousands of cases. Instead, only the shovelers themselves, who had breathed a heavy concentration of guano dust for days, got it.
The existence of bat virus RaTG13 is therefore not necessarily evidence of a natural bat origin. In fact, it seems to me to imply the opposite: New functional components may have been overlaid onto or inserted into the RaTG13 genome, new Tinkertoy intermolecular manipulations, especially to its spike protein, which have the effect of making it unprecedentedly infectious in human airways.
This is where the uniquely peculiar furin insert and/or the human-tuned ACE2-receptor-binding domain may come in — although it’s also possible that either of these elements could have evolved as part of some multistep zoonotic process. But in the climate of gonzo laboratory experimentation, at a time when all sorts of tweaked variants and amped-up substitutions were being tested on cell cultures and in the lungs of humanized mice and other experimental animals, isn’t it possible that somebody in Wuhan took the virus that had been isolated from human samples, or the RaTG13 bat virus sequence, or both (or other viruses from that same mine shaft that Shi Zhengli has recently mentioned in passing), and used them to create a challenge disease for vaccine research — a chopped-and-channeled version of RaTG13 or the miners’ virus that included elements that would make it thrive and even rampage in people? And then what if, during an experiment one afternoon, this new, virulent, human-infecting, furin-ready virus got out?
For more than 15 years, coronavirologists strove to prove that the threat of SARS was ever present and must be defended against, and they proved it by showing how they could doctor the viruses they stored in order to force them to jump species and go directly from bats to humans. More and more bat viruses came in from the field teams, and they were sequenced and synthesized and “rewired,” to use a term that Baric likes. In this international potluck supper of genetic cookery, hundreds of new variant diseases were invented and stored. And then one day, perhaps, somebody messed up. It’s at least a reasonable, “parsimonious” explanation of what might have happened.
This may be the great scientific meta-experiment of the 21st century. Could a world full of scientists do all kinds of reckless recombinant things with viral diseases for many years and successfully avoid a serious outbreak? The hypothesis was that, yes, it was doable. The risk was worth taking. There would be no pandemic.
I hope the vaccine works.